The concept of Six Sigma in project management
Motorola received a lot of complaints in 1986 about the huge number of manufacturing defects found in their products. Realizing that the situation needed to be urgently corrected, Chief Engineer Bill Smith developed the Six Sigma method to keep defects to a minimum during the development process.

The very concept of Six Sigma is taken from the theory of probability. One of its formulas states that there should be no more than 3.4 defects per million products or processes. Thus, the goal of the technique is to reduce the dispersion of variants. In simple terms, Six Sigma is an approach to project management and is focused on eliminating production errors.
The principles for implementing Six Sigma are:
- Control workflows so that they become predictable
- Ensure that all manufacturing and business processes can be described, analyzed, customized, or measured
- Involve management professionals and all of the teams involved in the work
- Set specific SMART goals that can be measured. For example, cut production costs by 15%
- Attract managers with strong leadership qualities and developed communication skills
- Make decisions only on the basis of confirmed information and statistics
Six Sigma method: DMAIC algorithm

In practice, Six Sigma is actually a step-by-step improvement on an existing process that will even work for newcomers to project management. DMAIC is an abbreviation made up of:
- Define
- Measure
- Analyze
- Improve
- Control
Therefore, each project goes through the following five stages:
- Define the project's goals, the current situation, key problems, and the customer's needs. Form a team to work on fixing bugs and then define areas of responsibility and authority for each specialist. For example, your problem is too many bugs in the final version of the website.
- Collect actual data on the situation; "measure" the main parameters of the process. You need to understand the level and complexity of the problem. For example, the team is great at developing business card sites, but complex and structured sites are poorly developed.
- Analyze the collected information and identify the factors affecting the quality of the company and its work processes. You need to identify the most important causes of errors (defects) and then choose the best way to eliminate them. For example, the quality of sites is affected by the lack of proper experience of the team or difficulties in communication between departments.
- Improve the current "problem" processes. At this stage the changes should be tentative. You also need to make a list of "mistakes to work on" so that you can not only correct them, but also not repeat them again. For example, send your team to a special training on website development.
- If the proposed changes had a positive effect on performance, then make them permanent. At this point, you should have set up mechanisms to manage changes so that they don't cause deviations from the goals of the project, otherwise it will be full of defects. Monitor the statistics and keep improving the process incrementally until you reach the desired quality level. For example, you can test the site for bugs after the introduction of each new element in order to identify them "at the root".

Six Sigma tools
Here you can use the following quality management methods:
- "5 whys". You will need to assemble a development team (it is possible in an informal setting) and arrange a brainstorming session. Ask each other the question "Why did this happen? Why is it so?" until the root cause of the defect emerges.
- Map of business processes. A schematic representation of the available resources and the tasks of the project. This will be used to decide what resources you have and what needs to be done.
- Experiment. Testing a solution on a group from the target audience.
- Cost/ benefit analysis. When faced with a choice between several project options, choose the one with the best cost to benefit ratio.
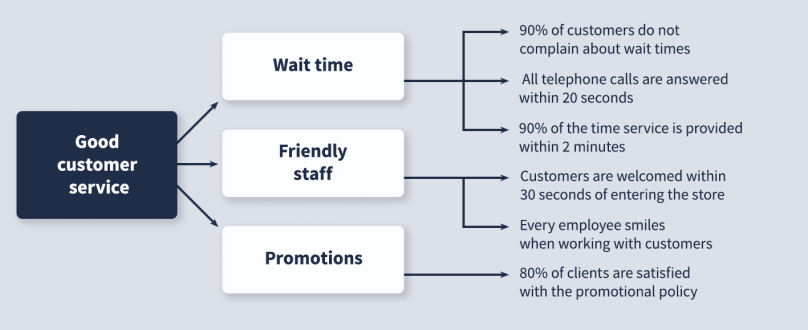
- CTQ tree - a "tree" of indicators that are critical to quality. This is an excellent tool for managing the quality of services, products, or the very work of a company. Draw a diagram of the key characteristics that are most important to your project. For example, here's the tree for a children's store:
Implementing Six Sigma can also be achieved by using statistical tools such as:
- Pareto curve
- Scatter chart
- Shewhart control chart
- Regression analysis
- Variance analysis
Lectera’s Online Courses by topic
The concept of Six Sigma: a hierarchy of specialists

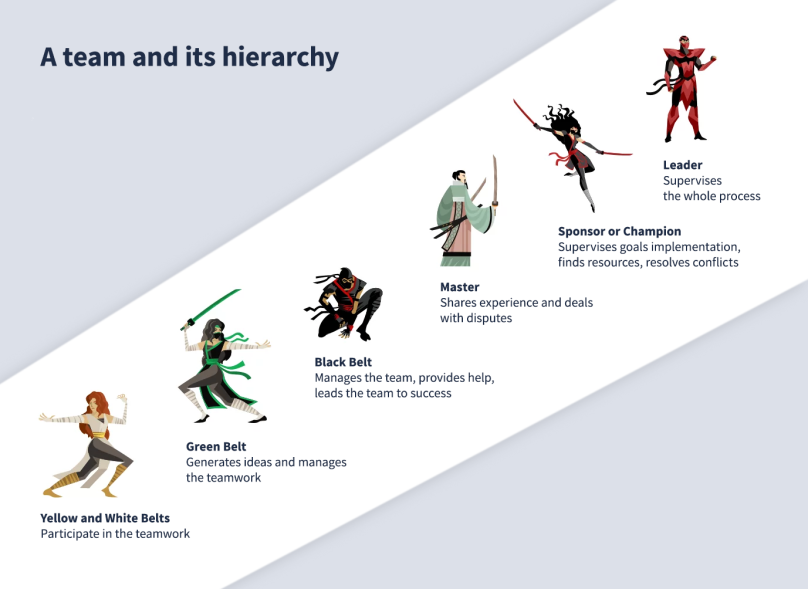
The Six Sigma method symbolically appeals to oriental martial arts. The role of each specialist on a project team depends on their belt. The color of the belt is the level of knowledge and skills required to learn Six Sigma. The "pyramid" of specialists is built as follows:
- At its top and at the head of the project is the Leader. He assigns tasks, authority, and resources. He is also responsible for effective communication between team members, conflict resolution, and overcoming employees' resistance to change.
- Champions have adopted Six Sigma and organize their work according to the new rules. They are also the mentors of the Black Belts .
- Master Black Belts oversee the implementation of Six Sigma and command the ordinary Black Belts.
- Ordinary Black Belts lead the project and carry out the tasks assigned by the Leader. The Black Belt master attends to them throughout the project.
- Green Belts are team members that, like the Champions, are responsible for implementing the method, in addition to their main responsibilities which includes keeping an eye on the Green Belts and Black Belts.
- Sometimes, in addition to Green belts, White Belts and Yellow Belts are present. These are the employees of the company who already know the Six Sigma method at a basic level, periodically participate in the project, or receive Six Sigma training from more experienced colleagues as outside observers. The Yellow Belt is slightly higher in awareness than the White Belt, but the difference is negligible so they are often put on the same level as the Yellow Belts.
Lean Six Sigma
Besides the classic approach, there is also Lean Six Sigma. It combines the benefits of Six Sigma and Lean. The result is a set of methods for managing production and business processes that can improve any company of any structure and industry.
"Lean Manufacturing" was created in Japan back in the 1960's by the ideologist of "Toyota" Taiichi Ohno. It is based on an Eastern philosophy which consists of the idea that perfect order should reign in all processes of a company. It wasn't until 1990 that this concept spread to the United States, and to this day its principles remain unchanged.
- The key to reducing manufacturing defects and delivering high quality work is a commitment to employee success. In order to do this, everyone should be given the same conditions for professional growth and the realization of their ambitions.
- Management and change management should be based not only on technology and rules, but also on the use of human resources. This in itself is the best quality management tool.
- Much depends on an effective corporate culture. Its continuous improvement in order to increase the comfort and cohesion of employees is one of the priorities of a successful company.
- The leader of the company acts as the "leader of the pack". It is he who must identify problems and the causes of errors in a timely manner, as well as maintain a favorable climate on his teams.

So what is Lean Six Sigma that combines all of the above with Six Sigma? These are the most valuable advantages of both methodologies, offsetting the disadvantages of each other. For example, "lean manufacturing" does not impose any requirements on the production infrastructure and shifts all responsibility to managers and their personal qualities. The strategy of Six Sigma distributes this responsibility. Moreover, it is focused on customer satisfaction, while "lean manufacturing" is more concerned with reducing costs. The concept of "lean manufacturing" teaches that manufacturing defects are the main cause of financial losses, while Six Sigma provides a concrete method for eliminating costs and correcting errors. Thus, both methodologies complement each other. And if Lean is a philosophy, then Six Sigma is a tool.
Many training programs for Lean Six Sigma and the classical approach of Six Sigma are specifically designed for beginners. It is best to start small and become familiar with one of these concepts before combining them. But both are must-haves for companies that want to improve the quality of their work and thereby reach a new level of trust with their customers.
Lectera’s Online Courses by topic
Share this with your friends via:
Latest News

In the UK, £23 million has been allocated for the expansion of the EdTech Testbed program — pilots of educational technologies in schools and colleges.

In the US, Tuskegee University announced the launch of Tuskegee University Global Campus (TUGC) — a new online platform for distance learning.

A significant stage in the development of the alternative education system has begun in West Northamptonshire in the UK: the County Council is actively calling on parents, guardians, and trustees to participate in shaping the future of this key area.

Outwoods Primary School in Atherstone, Warwickshire, having experienced deep sadness after the loss of their famous cat, Silla, has found solace in a new pet – a Maine Coon named Aloysius O’Hara.

In modern universities, artificial intelligence, and in particular ChatGPT, is rapidly transforming from a controversial tool into a full-fledged student assistant.









 Spring skills audit: what to remove, strengthen, and “sow” in learning
Spring skills audit: what to remove, strengthen, and “sow” in learning
 9 Career Mistakes Young Professionals Make
9 Career Mistakes Young Professionals Make
 £23 million allocated for the expansion of EdTech Testbed in the UK
£23 million allocated for the expansion of EdTech Testbed in the UK
 Test: How Psychologically Mature Are You? Check Your Inner Foundation.
Test: How Psychologically Mature Are You? Check Your Inner Foundation.
 Test. Check Your Social Media Dependency Level!
Test. Check Your Social Media Dependency Level!
 Test: What Business is Right For You?
Test: What Business is Right For You?